INTERNAL ASSESMENT
2022-23
SEMESTER- IV
Question Bank
SKILL ENHANCEMENT
COURSE-: Mushroom Culture technology
1.
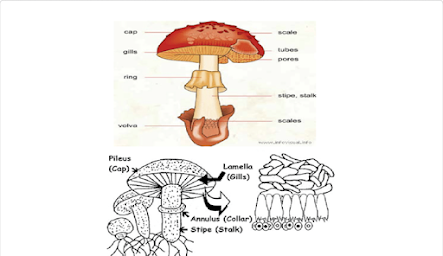
Define mushroom__________________________________________________
2.
What is mother spawn- mushroom fungus grown on a grain based medium
3.
What are the products that can be made from mushrooms?__ We can make various products
like soup powder, papad, nuggets, chips, preserve, candy, etc using different mushrooms. products like
pasta, noodles, etc by supplementing with fresh or dried mushroom powder._
4.
What is spawn? The seed material of
mushroom fungi is called Spawn
5.
Name any two species of mushrooms which are cultivated and edible—
1.Agaricus bisporus (button mushroom), 2.Pleurotus spp. (oyster mushroom)
6.
What type of climate is suitable for mushroom cultivation –
Mushroom
prefer a cool environment with temperatures around 70 degrees
Fahrenheit.
7.
What substrate is used for growing mushrooms_
The
main nutrients are less nitrogen and more carbon so materials containing cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin (i.e., rice and wheat straw, cotton seed
hulls, sawdust [SD], waste paper, leaves, and sugarcane residue) can be used as
mushroom substrates
8.
Write any two
poisonous mushrooms –
Amanita phalloides (death cap) ,
Amanita muscaria (fly Agaric)
9.
What is the other
name of
Mushrom?
A. Funaria B.
Dryopteris C. Agaricus D.Ferus
10.
To which division
does mushroom belong?
A. Basidiomycetes B. Thalophyta
C. Mollusca D.Algae
11.
When are mushrooms
grown?
A. year-round. B.winter C. summer D.
spring season
12.
The gills on either
sides bear club shaped basidia which produce
A. Basidiocarp B.Chloroplasts
C. Funaria gill F.None of the above
13.
What is a symptom of
mushroom poisoning?
A. Mild
nausea B. Vomiting C. Diarrhea D.all of the these
14.
Where is National
Centre for Mushroom located in India._____________
A. Solan,
Himachal Pradesh B. sangareddy,Telangana C. Guntur,Andhra
Pradesh D.none of these
15.
Edible part of
mushroom is:
A. Basidiocarp B.Secondary
mycelium C. Primary
mycelium D. Basidiospores
16.
It grows during ___________
A. Summer
season B. Winters C. Rainy season D. In all seasons
17.
Mushroom is ___________
A. Saprophytic
fungus v B. Autotrophic Algae C. Heterotrophic fungus D.
None of the above
18.
When young fruit body is completely enveloped by a thin membrane,it is
called
A. Mycelium B.
Rhizoids C. Velum (veil) D. Septae
19.
On the lower side of Pileus number of vertical plates like structure are
present called _
A. Spores B.
Organelles C. Mushroom Dryopteris D. Gills
20.
What does the name of the Maitake mushroom mean ?
A. Dancing
mushroom B. Lover of he dawn C. Born from the
rain D. Mother of Earth
21.
Oyster mushrooms are used to
treat what medical condition?
A. Measles B.
Viral infections C. High cholesterol levels D.
Liver disease
22.
In What climate zone does the popular Parasol mushroom grow?
A.Temperate B.
Tropical C. Boreal D. All of these
23.
Spawning : The spawn is spread over the
surface of the bed and covered with a thin layer of compost
24.
Casing –The process of covering the mycelial
mat on compost, surface is made with a thin layer of soil mixed with different
substances
25.
Agaricus bisporus belongs to family_________. a. Agaricaceae b.
Malvaceae c. Rubiaceae d. Solanaceae
26.
Short method of button mushroom compost preparation requires_____ days.
a. 14-18 days b.
10 days c. 20
days d. 30 days
27.
Mycellium produces white or colored umbrella shaped fruiting bodies
called:
a.
Haphae b.
Basidiocarp c.
Annalus d. Seta
28.
When young fruiting body is completely enveloped by a thin membrane, it
is called
a. Mycelium b.
Rhizoids c. Velum(veil) d. Septate
29.
Spawn is the ……. Of Mushroom
a. Spores b.
Mycellium c. Fruit d. Both a and b
30.
What is the mode of nutrition of Mushroom
a. Photosynthetic b.
Chemosynthetic c. Saprophytic d.
None of the above
31.
The poisonous or inedible species of fungi are known as
a. Mushrooms b. Bracket
fungi c. Toad stools d. Saprophytic fungi
32.
For long term storage mushrooms are stored in
a. Acid solution
b. Alkaline solution c. Salt solution d. Alcohol
33.
Canning Is employed for ….
a. long term storage b.
short term storage c. both d. none of the above
34.
Centre of tropical mushroom research and training (CTMRT) located in
a. Bhubneshwar b.
Nagaland c. Andrapradesh d.Manipur
35.
Indira Gandhi Krishi vishva Vidyalaya , located in …
a. Bhubneshwar b. Raipur c.
Andrapradesh d.Manipu
36.
During Spawining temperature should be maintain between..
a. 20-30 b.
55- 70 c.
80-100 d. 0-10
37.
Mushroom has
a. Anticancer
property b. Anti-aging property c. Antibiotic property d. All of the
above
38.
Agaricus bisporus belongs to family_________.
a. Agaricaceae b. Malvaceae
c. Rubiaceae d. Solanaceae
39.
Basidiospores are___________spores.
a. exogenous b. endogenous
c. Both a and b d. None of these
40.
toxin is present in Amanita muscaria.
a. Ibotenic acid b. Lactic acid c. Acidic acid d. All of the above
41.
Formaldehyde is used as__________in mushroom
cultivation.
a. Disinfectant b. Fertilizer c. Insect repellant d. Food material
42.
Short method of button mushroom compost preparation requires_____
days.
a. 14-18 days b. 10 days c. 20 days d. 30 days
43.
Mushroom is:
a. Saprophytic fungus b.
Autotrophic Algae c. Heterotrophic
fungus d. None of the above
44.
Basidiocarp consist of a fleshy stalk called
___________ and umbrella like head borne
on its top called __________
a. Hyphae and Seta b. Seta and Annalus c. Annalus adn Antheridia d. Stipe
and Pileus
45.
When young fruiting body is completely enveloped by a thin
membrane, it is called
a. Mycelium b. Rhizoids c. Velum(veil)
d. Septate
46.
It grows during ______
a. Summer season b. Winters c. Rainy
season d. In all seasons
47.
Brown coloured dye is
obtained from ..
a. Polyporus
bispidus b. Agaricus bisporus c. Gonoderma frondosa d. Amanita muscaria
48.
Amanita muscaria is ….
a. Edible b.
Poisonous c. Non poisonous d. none of the above
49.
Indira Gandhi Krishi vishva
Vidyalaya , located in …
a. Bhubneshwar b. Raipur
c. Andrapradesh d.Manipur
50.
Mushroom training centre in
Tamilnadu is
a. Agriculture
college and research institute b.Angara village industries c. Mushroom
production and training centre d.
farmer training centre
51.
Following materials are used
for packing of mushroom ..
a. Fibre board trays b.
Polyethylene c. Paper d. none
52.
Preservation methods of
mushrooms are ….
a. pickling b. Canning c. both
d. None of the above
53.
Paddy straw mushroom is a. Agaricus bisporous
b. Volvariella volvacea c. Plurotus sajourkaju d. Auricularia species
54.
Give the medicinal benefits of mushrooms
Medicinal
values of the some important mushroom are given below:
1.
Good for heart
The
edible mushrooms have little fat with higher proportion of unsaturated fatty
acids and absence of cholesterol and consequently it is the relevant choice for
heart patients and treating cardiovascular diseases.
2.
Low calorie food
The
diabetic patients choose mushroom as an ideal food due to its low calorific
value, no starch, little fat and sugars. The lean proteins present in mushrooms
help to burn cholesterol in the body. Thus it is most preferable food for
people striving to shed their extra weight.
3.
Prevents cancer
All
forms of edible mushrooms, and white button mushrooms in particular, can
prevent prostate and breast cancer. Fresh mushrooms are capable of arresting
the action of 5-alpha-reductase and aromatase, chemicals responsible for growth
of cancerous tumors. The drug known as Polysaccharide-K (Kresin), is isolated
from Trametes versicolor (Coriolus versicolor), which is used as
a leading cancer drug.
4.
Anti-aging property
The
polysaccharides from mushrooms are potent scavengers of super oxide free
radicals. These antioxidants prevent the action of free radicals in the body,
consequently reducing the aging process. Ergothioneine is a specific
antioxidant found in Flammulina velutipes and Agaricus bisporus which
is necessary for healthy eyes, kidney, bone marrow, liver and skin.
5.
Regulates digestive system
The
fermentable fiber as well as oligosaccharide from mushrooms acts as a
prebiotics in intestine and therefore they anchor useful bacteria in the colon.
This dietary fibre assists the digestion process and healthy functioning of
bowel system.
6.
Strengthens immunity
Mushrooms
are capable of strengthening the immune system. A diverse collection of
polysaccharides (beta-glucans) and minerals, isolated from mushroom is
responsible for up-regulating the immune system.
55.
What is spawn?
56.
Name some foods prepared from mushrooms.
57.
Name 2 poisonous mushrooms.
58.
Give the classification of Agaricus
bisporus
Define mushroom
A mushroom, also called toadstool, is the
fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above
ground on soil or on its food source. The fleshy, edible fruit bodies of
numerous macrofungal species are called edible mushrooms.